We have created an article summarizing the scope of representation when applying for refugee recognition in Japan ” refugeesjapan “
The Original article in Japanese
Below is the article translated into English by Google Translate.
While there are arguments that Japan is harsh on refugees and that it should accept more refugees, there is also a deep-rooted cautious view of whether Japan can really accept them, just like it does with immigrants. From June 10th, the deportation procedures will be made stricter, and if the application is unsuccessful three times, the amendment will basically be deported. With the mass evacuation of Ukrainians from February 2022, we have created a special refugee status that has never been seen before in Japan. This case may be the spark that will change future refugee policy, and I am curious about the direction it will take. We will explain the basics of applying for refugee recognition.

History of applying for refugee recognition in Japan
With the Convention Relating to the Status of Refugees and the Protocol Relating to the Status of Refugees (hereinafter referred to as the “Protocol”) coming into force in Japan in 1982, a refugee recognition system was established in Japan.
Definition of refugee
(2) as a result of an incident that occurred before January 1, 1951, and who is at risk of persecution because of race, religion, nationality, membership in a particular social group, or political opinion; A person who is outside the country of his nationality and is unable to avail himself of the protection of that country because he has a well-founded fear of and stateless persons who, as a result of these events, are outside their country of habitual residence and are unable or fearful of returning to their country of habitual residence. A person who does not wish to return to the country of his or her habitual residence in order to have possession of the same.
In the case of a person who has more than one nationality, “country of nationality” means any country of which the person is a national, and where there is a justifiable fear of persecution. Even if a person does not receive the protection of one of the countries of his nationality without valid reasons, it cannot be recognized that he does not have the protection of his country of nationality.
refugee requirements
The requirements for a refugee as defined in Article 1A(2) of the Refugee Convention are:
(a) have a well-founded fear of being persecuted because of race, religion, nationality, membership of a particular social group, or political opinion;
(b) be outside the country of nationality;
(c) is unable to avail himself of the protection of his nationality, or is unwilling to avail himself of the protection of his nationality because of such fear;
Changes in refugee recognition applications in Japan
The background to Japan’s accession to the Refugee Convention is that discussions on refugee issues rapidly increased in Japan following the mass exodus of Indochinese refugees in the early 1975s.
Upon acceding to the Refugee Convention, the existing immigration control laws and regulations were revised, a new refugee recognition system was introduced, and the name of the law was changed to the “Immigration Control and Refugee Recognition Act (Immigration Control Act).” The Immigration Services Agency of the Ministry of Justice is responsible for determining whether a foreign national falls under the category of refugee as defined in the Refugee Convention (refugee recognition).
The number of applications from the introduction of the refugee recognition system in 1982 to 2021 was 91,664, of which 1,117 (1.2%) were recognized as refugees, while those who were not recognized as refugees received humanitarian consideration. There were 5,049 people (5.5%) who were granted permission to stay in Japan.
Japanese refugee recognition application procedure
Refugee recognition is based on the documents submitted by the applicant and the applicant’s statements. Therefore, applicants are required to prove their refugee status on their own.
In addition, if sufficient proof cannot be obtained from the documents submitted by the applicant, the refugee inquirer will make inquiries to public offices, etc. to investigate whether the applicant’s allegations are true or not, and the applicant will be recognized as a refugee. We will make every effort to ensure that this is done properly.
Ref:Refugee recognition procedures/supplementary protection recipient recognition procedures
Refugee recognition application procedure
Four types of documents are required when applying. In particular, materials proving that the applicant is a refugee or a statement claiming refugee status must be carefully prepared.
- Application form for recognition of refugee/supplementary protection status
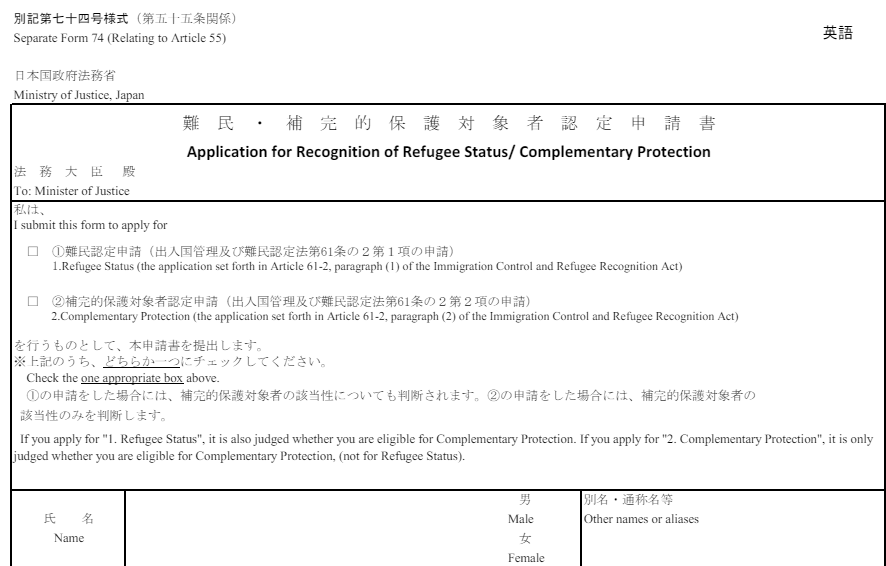
- Photo (length 4cm x width 3cm)
- document proving that the applicant is a refugee or a person subject to supplementary protection (or a statement claiming that the applicant is a refugee or a person subject to supplementary protection)
- following documents:
a. Passport or certificate of residence status ( foreign national who cannot present their passport or certificate of residence status, please submit one document stating the reason.)
b. Residence card (if you have one)
c. Foreign nationals who have received permission for provisional landing, permission for crew landing, permission for emergency landing, permission for landing due to distress, or landing permission for temporary asylum should submit their permission.
d. Foreign nationals on provisional release must obtain a provisional release permit.
Provisional release is a release from detention based on a deportation order, and provisional stay is a release from detention while an applicant is applying for refugee status.
Permission for temporary stay
When an application for refugee recognition is received from a foreigner who has not obtained a status of residence, such as an illegal alien, the government will temporarily allow them to stay in Japan, and deportation procedures will be suspended during that time.
- When the foreign national has applied for refugee recognition within six months from the date of landing in Japan in order to stabilize the legal status of the foreign national.
- Or if the person meets certain requirements, such as when the person entered Japan directly from a territory where there was a risk of persecution under the Refugee Convention.
Please note that the determination of permission for provisional stay will be made based on the documents submitted by the applicant for refugee recognition, such as the Application for Recognition of Refugee/Supplementary Protection Person, so there is no need to apply separately for permission to stay.
(1)Stay with temporary residence permit
You can stay in Japan legally until the relevant permission ends, such as after the period of temporary stay has passed.
(2)temporary residence permit
A temporary residence permit will be issued to foreign nationals for whom the Minister of Justice has granted permission for temporary residence.
(3)Period of temporary stay and extension of the same period
As a general rule, the temporary stay period is June.
(4)Conditions for temporary residence permit
Foreign nationals who receive a temporary residence permit are restricted in their residence and range of movement, and are also prohibited from working in Japan. Additionally, if you are requested to appear by a refugee investigator, various conditions will be attached to you, such as the obligation to appear at a designated date, time, and location and cooperate with refugee recognition procedures.
(5)Cancellation of permission for temporary stay
If a foreigner who has been granted permission for provisional stay violates the conditions attached, if he submits forged or altered materials for the purpose of fraudulently receiving refugee recognition, or if he makes a false statement, etc., he will be granted provisional stay. permission may be revoked.
Ref: Refugee recognition system
Rights or benefits that can be enjoyed by refugee recognition
Foreign nationals who have been recognized as refugees are entitled to the following rights and benefits:
1 Granting a stable status of residence
In principle, you will be granted the residence status of “Long Term Resident”.
2 Partial relaxation of permanent residence permit requirements
Foreign nationals who have been recognized as refugees and reside in the country can receive a permanent residence permit at the discretion of the Minister of Justice, even if they do not meet the requirements of having sufficient assets or skills to earn an independent living.
3 Issuance of refugee travel document
Foreign nationals who hold a refugee travel document can leave and enter Japan as many times as they wish within the validity period stated on the certificate.
4 Various rights stipulated in the Refugee Convention
In principle, they are treated in the same way as nationals of contracting countries or general foreigners, and in Japan they are eligible to receive national pensions, child rearing allowances, welfare allowances, etc., and are treated the same as Japanese nationals. I can.
What is provisional release?
As a result of the violation investigation, if there is sufficient reason to suspect that the suspect falls under the grounds for deportation, the suspect will be detained based on a detention order issued by the chief examiner of the Regional Immigration Bureau.
There is a system of provisional release, and there are opportunities for visits and visits during detention.
Provisional release is a system in which the detention of a detainee is temporarily suspended, upon request or ex officio, and the detention of the detainee is temporarily released with certain conditions attached.
Although detention under a deportation order is stipulated “until deportation is possible,” it may be necessary to temporarily release the detainee for health reasons, preparations for departure, etc. It was established to deal with such cases.
The period of detention according to the detention order is “30 days (however, if the chief examiner deems that there are unavoidable reasons, this can be extended up to 30 days).”
・ Who can request provisional release?:The detainee or his or her representative, curator, spouse, direct relative, or brother or sister
・ Where to apply for provisional release:If the detainee is being held in an immigration detention center, the director of the immigration detention center, or if the detainee is being held in a detention facility of a Regional Immigration Bureau, the Regional Immigration Bureau that has jurisdiction over the detention facility. chief examiner of
・ Documents to be submitted:In addition to one application for provisional release, materials certifying the reason for requesting provisional release, materials regarding the guarantor, etc.
If a request for provisional release is made, the person shall be provisionally released by making the person pay a deposit of 3 million yen or less, and subject to restrictions on residence and range of movement, obligation to appear in response to a summons, and other conditions deemed necessary. It is determined that this can be done.
Regarding security deposits, only when the director of the immigration detention center or the chief examiner deems it appropriate, a guarantee given by someone other than the detainee may be substituted for the security deposit. It must state the amount of the bond and the fact that the bond will be paid at any time.
Regarding cancellation of release, it is stipulated that if a foreign national who has been granted provisional release permission commits the following acts, the director of the immigration detention center or the chief examiner may revoke provisional release.
(1)escape
(2)There is sufficient reason to suspect that he will flee.
(3)Not responding to a call without a valid reason
(4)Violated other conditions attached to provisional release
If provisional release is revoked, the person who was provisionally released will be re-incarcerated and their security deposit will be forfeited based on a detention order or deportation order.
- Re-detained at immigration detention center or detention center of Regional Immigration Bureau
- In addition, the deposit paid at the time of provisional release will be confiscated.
Provisional release can be said to be a system similar to bail, as even if a person is incarcerated, they can be released by posting a surety bond.
The following temporary stays are exemptions from detention while applying for refugee status.
Summary of applying for refugee recognition in Japan
After accepting Indochinese refugees in 1975, Japan successively acceded to the 1951 Convention Relating to the Status of Refugees in 1981 and the Protocol Relating to the Status of Refugees in 1982. We have recognized such foreign nationals as refugees and provided appropriate protection. Nearly 40 years have passed since Japan joined the system, and even during that time it has been criticized internationally for its low refugee recognition rate and low number of applications.
On the other hand, in recent years, many people, such as conflict refugees, are at risk of persecution due to one of the five reasons under the Refugee Convention: race, religion, nationality, membership in a particular social group, or politics. There are foreign nationals all over the world who do not fall under any of the above opinions and do not fall under the category of “refugees” under the Convention, but who still require protection.
This time, we have explained the background behind how Japan recognized refugees and the refugee recognition procedures. I have also written about the rights that come with being recognized as a refugee, as well as measures to avoid long-term detention such as provisional stay and provisional release while applying for recognition, and the situation faced by applicants as they wait for their results.
Completing the Refugee/Supplementary Protection Status Application Form can be a daunting task. You will be asked to explain your family composition, educational background, work history, and the reason you became a refugee. Please contact an administrative scrivener who is an expert with the latest information.